
HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) is an analytical method extensively used in chemistry and biochemistry for the separation, identification, and quantification of components within a mixture. The explanation of the intricate details of its different phases like the ‘mobile’ and ‘stationary’ phase and ‘specialized column’ for the separation of compounds comes as a major challenge for educators when trying to simplify the subject. But this can’t lead to undermining the wide applications that this technique finds in drug analysis, environmental testing, and quality control across different industries.
Since it’s such an important technique for both academia and industry, we aim to provide 5 strategies that educators can utilize to ease the HPLC teaching for their next session.
Educators can use models and simulations for simplifying the scientific principles underlying HPLC. Studies have reported several benefits of using these new-world tools for teaching complex chemistry and biology topics. (1, 2)
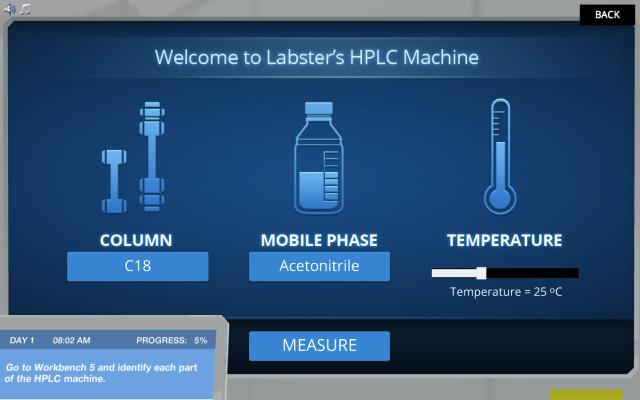
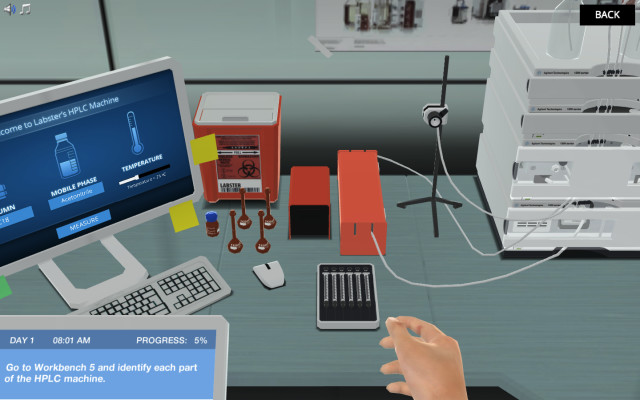
Educators can design different types of games and classroom-friendly activities to effectively facilitate student learning and simplify the science underlying HPLC. By incorporating interactive elements, these educational tools enhance student engagement and promote active learning.
Research has evidenced that physical as well as digital games provide a stimulating learning environment where students can apply HPLC principles in practical scenarios, reinforcing their understanding. Activities such as virtual experiments can encourage students to explore beyond the textbooks. Labster's Gamified HPLC Elements involves students in selecting apt mobile phases and columns which can reinforce a better understanding of HPLC techniques.
Educators can simplify the science underlying HPLC by incorporating different types of technological tools in their teaching strategies. Virtual reality (VR) can be used to demonstrate HPLC machine compartments, explain separation principles, and showcase parameter effects.
Labster infuses technology in innovative ways to simplify the core concepts of HPLC.

Discover Labster's HPLC virtual lab today!
There are diverse career paths that require candidates to be well-versed in the HPLC technique. Quoting such examples and highlighting the broad applicability of this technique across industries can be big motivators for students to hone their skills. You can introduce them to different online webinars and talks. You can directly correlate HPLC to its potential in professional growth and development by suggesting roles like:
Establishing a connection between HPLC and its real-world applications can profoundly motivate students by unveiling the practical significance and wide-ranging impact of the technique. Educators can choose to illustrate in their next class ‘how HPLC is employed in fields like pharmaceuticals, environmental analysis, and forensic sciences’.
By quoting such examples, students can recognize the tangible value of their knowledge in solving real-world problems. This connection imbues their learning experience with purpose and relevance. As a deepened sense of curiosity and motivation to excel in mastering HPLC techniques perspires, classroom teaching will immediately become more effective.
Teaching HPLC is crucial for students as it equips them with practical analytical skills and prepares them for careers in fields like pharmaceuticals, research, and quality control, where HPLC plays a vital role in analysis and problem-solving. Teachers need to be the problem-solvers when teaching HPLC, as they must address challenges related to understanding complex concepts and troubleshooting experimental issues necessary for the successful application of HPLC techniques in real-world scenarios.
Try our free 30-day All Access Educator's Pass today and teach with the HLPC simulation alongside 300+ other virtual labs!

Labster helps universities and high schools enhance student success in STEM.
Request DemoRequest a demo to discover how Labster helps high schools and universities enhance student success.
Request Demo