Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading 6
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.
Block quote
Ordered list
- Item 1
- Item 2
- Item 3
Unordered list
- Item A
- Item B
- Item C
Bold text
Emphasis
Superscript
Subscript
About This Simulation
Help determine what a bear ate before it died by building the structure and choose the internal organelles of the four basic types of animal cells found inside the bear’s mouth.
Learning Objectives
- Describe the different intracellular and extracellular components forming eukaryotic cells
About This Simulation
Lab Techniques
- Microscopic analysis
- Cell observation
Related Standards
- Early Stage Bachelors Level
- EHEA First Cycle
- EHEA Short Cycle
- FHEQ 4
- US College Year 1
- FHEQ 5
- FHEQ 6
- LS1.A-M2
- LS1.A-H1
- Biology Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function
- Biology 1.1 Introduction to cells
- Biology 1.2 Ultrastructure of cells
Learn More About This Simulation
This short, targeted simulation is adapted from the full-length “Cell Structure: Cell theory and internal organelles” simulation.
In this simulation, you will learn about the structures and internal organelles of animal cells. Physical structures of the four basic animal cell types will be highlighted and the function and importance of each internal organelle will be discussed. Oh, and you will have to take a tissue sample from inside the mouth of a bear. Watch out for the sharp teeth!
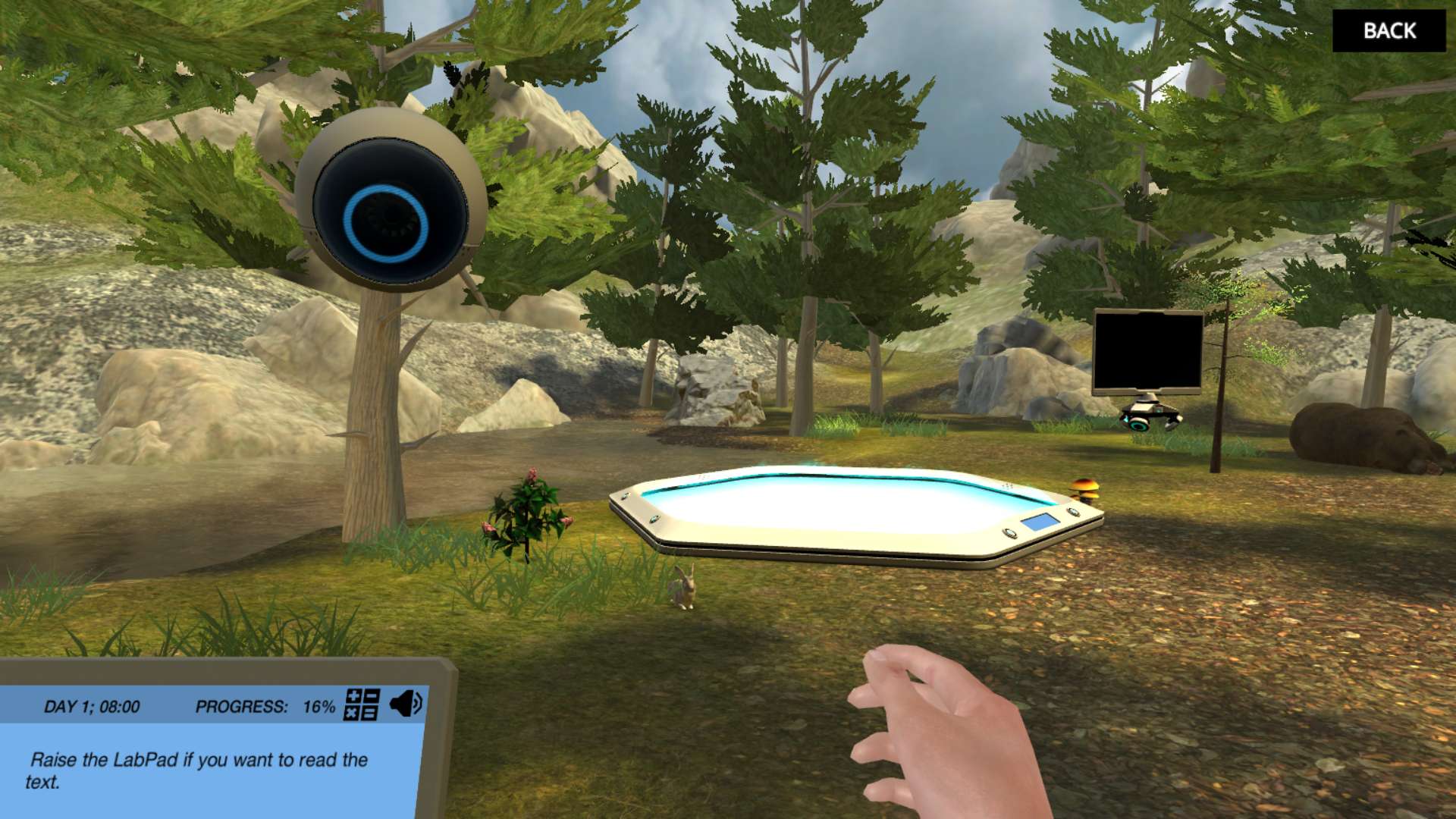
Investigate a bear’s death
Hikers have discovered a dead bear on their trail and it’s your mission to determine why it died. Maybe it was poisoned or maybe it died of underlying causes such as old age? Standing in the middle of a secluded forest, you must build up the courage to take a sample from inside the bear’s mouth. Then, build the potentially deadly organism by building 4 cells representative of each basic type of animal tissue: neural, epithelial, muscle and connective tissue.
Build the cells
Students will be challenged to choose the correct internal organelles for the animal cells. You will learn about the function and importance of the nucleus, ER, cytoskeleton, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, ribosomes, and mitochondria. Then, determine which cellular structures are unique to specific animal cells such as sarcomeres, tight junctions, axons, dendrites and the extracellular matrix.
Uncover the mysterious death of the bear Put together everything you have learned about organelles and cellular structures to build each type of cell in the mystery organism. At the end, will you be able to figure out what killed the bear and uncover the mystery?
For Science Programs Providing a Learning Advantage
Boost STEM Pass Rates
Boost Learning with Fun
75% of students show high engagement and improved grades with Labster
Discover Simulations That Match Your Syllabus
Easily bolster your learning objectives with relevant, interactive content
Place Students in the Shoes of Real Scientists
Practice a lab procedure or visualize theory through narrative-driven scenarios


FAQs
Find answers to frequently asked questions.
Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading 6
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.
Block quote
Ordered list
- Item 1
- Item 2
- Item 3
Unordered list
- Item A
- Item B
- Item C
Bold text
Emphasis
Superscript
Subscript
A Labster virtual lab is an interactive, multimedia assignment that students access right from their computers. Many Labster virtual labs prepare students for success in college by introducing foundational knowledge using multimedia visualizations that make it easier to understand complex concepts. Other Labster virtual labs prepare learners for careers in STEM labs by giving them realistic practice on lab techniques and procedures.
Labster’s virtual lab simulations are created by scientists and designed to maximize engagement and interactivity. Unlike watching a video or reading a textbook, Labster virtual labs are interactive. To make progress, students must think critically and solve a real-world problem. We believe that learning by doing makes STEM stick.
Yes, Labster is compatible with all major LMS (Learning Management Systems) including Blackboard, Canvas, D2L, Moodle, and many others. Students can access Labster like any other assignment. If your institution does not choose an LMS integration, students will log into Labster’s Course Manager once they have an account created. Your institution will decide which is the best access method.
Labster is available for purchase by instructors, faculty, and administrators at educational institutions. You can purchase Labster by speaking with a Labster sales representative. Compare plans.
Labster supports a wide range of STEM courses at the high school, college, and university level across fields in biology, chemistry, physics, and health sciences. You can identify topics for your courses by searching our Content Catalog.