Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading 6
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.
Block quote
Ordered list
- Item 1
- Item 2
- Item 3
Unordered list
- Item A
- Item B
- Item C
Bold text
Emphasis
Superscript
Subscript
About This Simulation
Finding the concentration of an acid can be tedious and boring. Join a science expert to learn how to drop the base in style!
Learning Objectives
- Assemble the apparatus required for titration
- Describe the function of each part of the titration apparatus
- Explain the general steps of a colorimetric acid-base titration and its uses
- Perform a titration experiment
- Describe the role of the 3 main reagents used in a titration: sample, titrant, and indicator
- Explain what is the endpoint of a titration and the role of the indicator
- Explain why the use of high-precision volumetric material is essential for a titration
- Calculate the concentration of the titrated solution from the results of the titration experiment
About This Simulation
Lab Techniques
- Acid-base titration
Related Standards
- HS-PS1-6, HS-PS1-7
- 4.6 Introduction to Titration
- 8.5 Acids-Base Titrations
- 8.2 Properties of Acids and Bases
- 8.3 The pH Scale
- 1.3 Reacting Masses and Volumes
Learn More About This Simulation
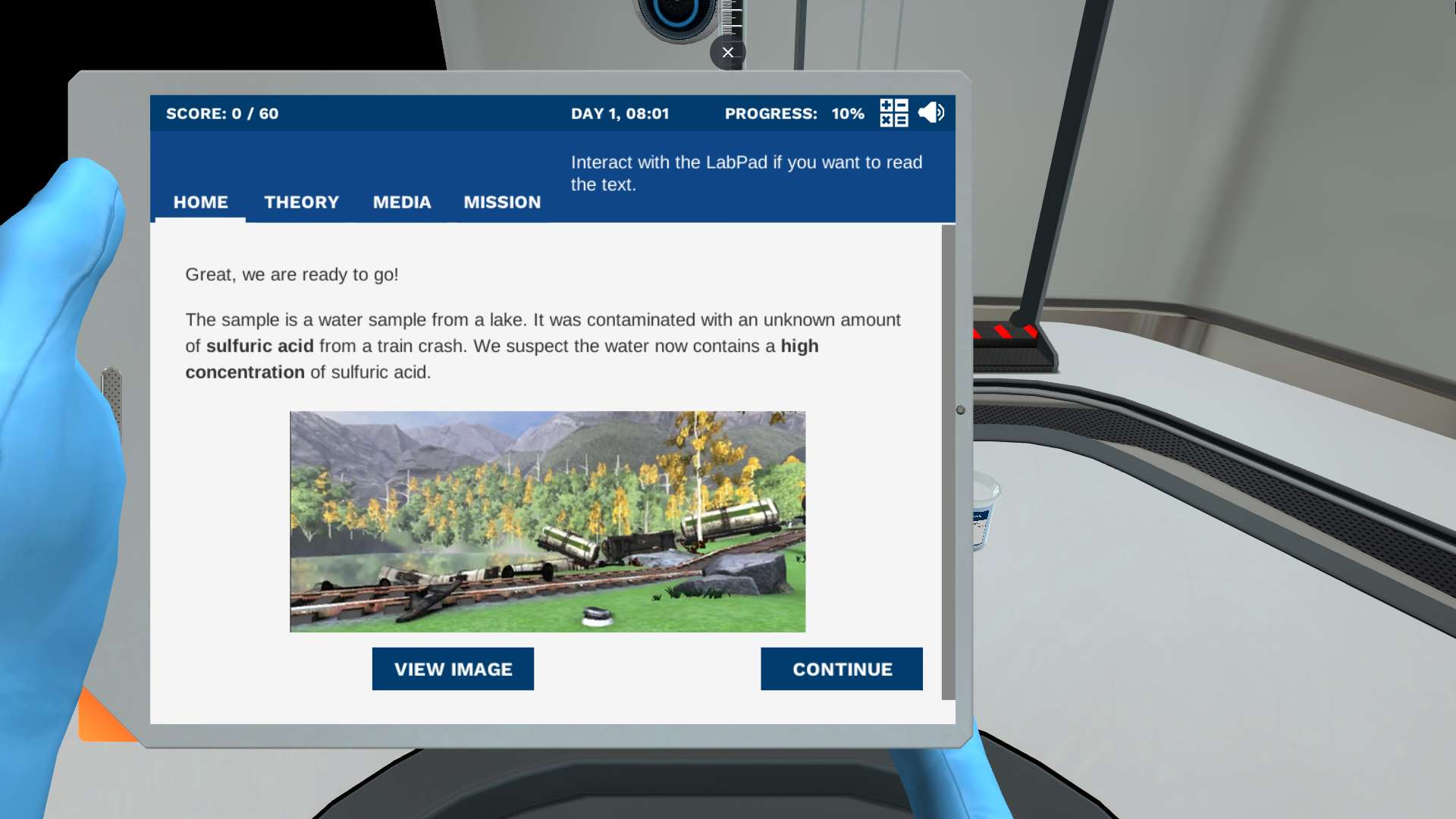
Counting potatoes in a bag would be pretty easy. You can feel, see, and touch the potatoes. Now imagine counting the amount of acid in a water sample. How would you do that? In this simulation, you will embrace the power of the titration technique. With appropriate lab apparatus, a chemical indicator and a base solution, you can determine the concentration of any acid.
Assemble the apparatus for titration
A successful experiment starts with good preparation. You will need a burette, a stand, a clamp and a flask to begin the titration procedure. Proper assembly of the apparatus is paramount to a successful titration. In this simulation, we will help you ace the assembly process so that once you go to the real-life lab, you will be able to Recognize and explain the function of each part of the apparatus used in the titration technique.
Performing titration
Once the assembly is complete, you are ready to drop the base! The best thing about this simulation is that you can perform the titration multiple times. But in science, many repetitions doesn’t always lead to improved accuracy. You have to figure out how many times you should repeat the experiment to achieve an accurate result. You also have the freedom to experiment with multiple indicators, various sample and titrant volumes.
Analyzing the titration results
Analyzing the titration results requires an understanding of the basic stoichiometry concept. You can try to do the analysis yourself or let us guide you through the analysis, where you’ll go through the method of determining the concentration of the acid step-by-step.
Will you be able to perform the titration and calculate the acid concentrations?
For Science Programs Providing a Learning Advantage
Boost STEM Pass Rates
Boost Learning with Fun
75% of students show high engagement and improved grades with Labster
Discover Simulations That Match Your Syllabus
Easily bolster your learning objectives with relevant, interactive content
Place Students in the Shoes of Real Scientists
Practice a lab procedure or visualize theory through narrative-driven scenarios


FAQs
Find answers to frequently asked questions.
Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading 6
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.
Block quote
Ordered list
- Item 1
- Item 2
- Item 3
Unordered list
- Item A
- Item B
- Item C
Bold text
Emphasis
Superscript
Subscript
A Labster virtual lab is an interactive, multimedia assignment that students access right from their computers. Many Labster virtual labs prepare students for success in college by introducing foundational knowledge using multimedia visualizations that make it easier to understand complex concepts. Other Labster virtual labs prepare learners for careers in STEM labs by giving them realistic practice on lab techniques and procedures.
Labster’s virtual lab simulations are created by scientists and designed to maximize engagement and interactivity. Unlike watching a video or reading a textbook, Labster virtual labs are interactive. To make progress, students must think critically and solve a real-world problem. We believe that learning by doing makes STEM stick.
Yes, Labster is compatible with all major LMS (Learning Management Systems) including Blackboard, Canvas, D2L, Moodle, and many others. Students can access Labster like any other assignment. If your institution does not choose an LMS integration, students will log into Labster’s Course Manager once they have an account created. Your institution will decide which is the best access method.
Labster is available for purchase by instructors, faculty, and administrators at educational institutions. You can purchase Labster by speaking with a Labster sales representative. Compare plans.
Labster supports a wide range of STEM courses at the high school, college, and university level across fields in biology, chemistry, physics, and health sciences. You can identify topics for your courses by searching our Content Catalog.